September has long been a pivotal month in the annals of stock market history. From the Great Depression to the dot-com bubble and beyond, this article delves into the key events and trends that have shaped the stock market during each decade of September.
1930s: The Great Depression
The 1930s were marked by the Great Depression, a period of severe economic downturn that began in 1929. September of 1937 saw the stock market crash, which was a precursor to the Great Depression. The market experienced a significant decline, and investors were left reeling from the loss of their investments.
1940s: World War II and Post-War Recovery
The 1940s were dominated by World War II, which had a profound impact on the stock market. During the war, the stock market was relatively stable, as the government implemented price controls and rationing. However, after the war, the market experienced a significant boom as the economy recovered and the U.S. emerged as a global superpower.
1950s: The Post-War Boom
The 1950s were characterized by a period of economic growth and stability. The stock market experienced a steady rise, driven by the expansion of the manufacturing sector and the growth of the middle class. The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) reached an all-time high in 1954, reflecting the strong economic conditions of the time.
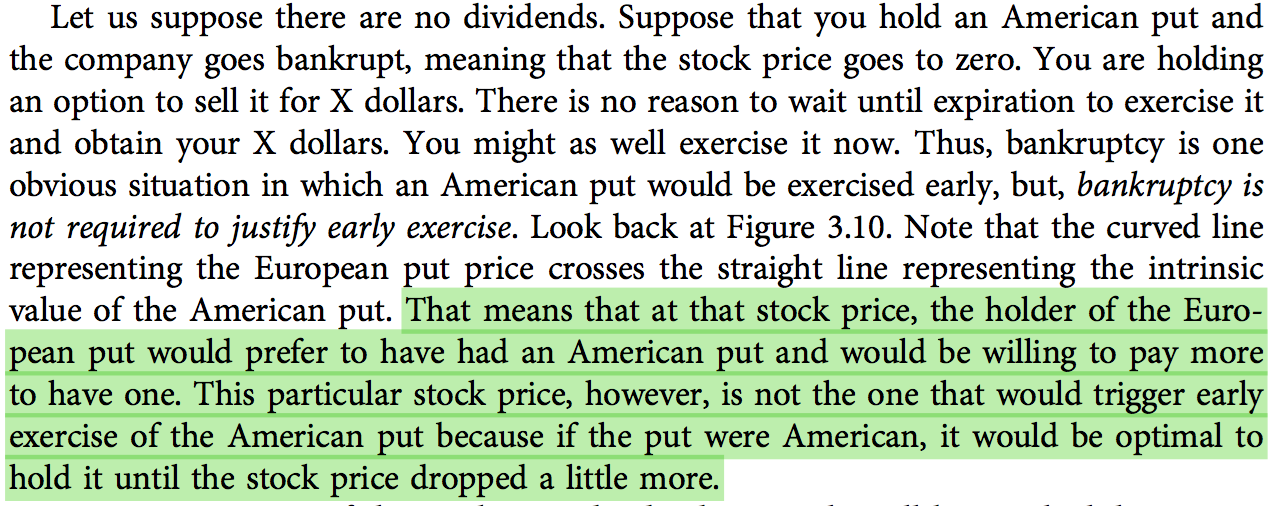
1960s: The Dot-Com Bubble
The 1960s saw the rise of the dot-com bubble, which was fueled by the growth of the technology industry. Many investors flocked to tech stocks, leading to a significant increase in stock prices. However, the bubble burst in 2000, causing a major market crash and leading to a period of economic uncertainty.
1970s: Oil Crisis and Inflation
The 1970s were marked by the oil crisis and high inflation. The stock market experienced significant volatility, as investors grappled with rising energy prices and rising interest rates. The market saw a period of stagnation, with the DJIA barely moving from its 1972 peak.
1980s: The Reagan Boom
The 1980s were characterized by the Reagan boom, a period of economic growth and low inflation. The stock market experienced a significant rise, driven by the expansion of the tech industry and the deregulation of financial markets. The DJIA reached an all-time high in 1987, reflecting the strong economic conditions of the time.
1990s: The Dot-Com Bubble
The 1990s saw the dot-com bubble reach its peak. Many investors flocked to tech stocks, leading to a significant increase in stock prices. However, the bubble burst in 2000, causing a major market crash and leading to a period of economic uncertainty.
2000s: The Financial Crisis
The 2000s were marked by the financial crisis of 2008, which was caused by the collapse of the housing market and the subsequent credit crunch. The stock market experienced a significant decline, with the DJIA falling by nearly 50% from its peak in 2007.
2010s: Recovery and Growth
The 2010s saw the stock market recover from the financial crisis and experience significant growth. The DJIA reached an all-time high in 2018, reflecting the strong economic conditions of the time.
In conclusion, September has been a pivotal month in the annals of stock market history. From the Great Depression to the dot-com bubble and beyond, the stock market has experienced significant changes and challenges over the years. Understanding the key events and trends of each decade can help investors make informed decisions in the future.
stock technical analysis